冒泡排序
分析
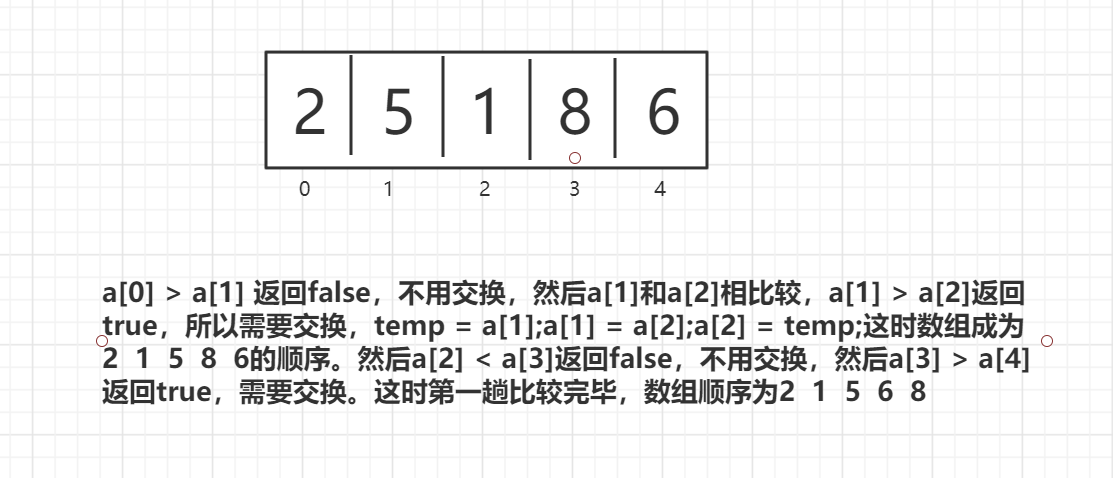
冒泡排序的思想是相邻两个数相比较,如果是按照从小到大的顺序排序,那么前一个数和后一个数相比较,如果前一个数大于后一个数,那么就需要把两个数交换,直到把所有的数都比较完,然后就把最大的数冒出来了。这是第一趟,每一趟都会冒出一个数,冒出的数,在下次比较时不用在参与比较,所以每次比较的次数都是上一次减一。比较的趟次是数组大小减一。因为一个数组中的数当前n-1个数的位置都确定了,那么第n个数的位置也就确定了。
图解
代码实现
package top.lukeewin.demo21;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2, 5, 1, 8, 6};
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(a));
bubbleSort(a);
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(a));
}
//冒泡排序
public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
int temp = 0;//用于交换
boolean flag = false;//标志位,标志是否是前一个数大于后一个数
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {//趟次
for (int j = 0; j < a.length - i - 1; j++) {//每趟比较的次数
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
//交换
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
优化后的代码
这里增加了一个flag标志位,标志一趟比较中是否发生过交换,如果没有发生过交换,则直接结束最外层循环,即本身数组就是有序了。
package top.lukeewin.demo21;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2, 5, 1, 8, 6};
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(a));
bubbleSort(a);
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(a));
}
//冒泡排序
public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
int temp = 0;//用于交换
boolean flag = false;//标志位,标志是否是前一个数大于后一个数
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {//趟次
for (int j = 0; j < a.length - i - 1; j++) {//每趟比较的次数
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
flag = true;
//交换
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
if (!flag) {//如果在一趟排序中没有发生交换,那么直接结束最外层循环
break;
}else {
flag = false;
}
}
}
}
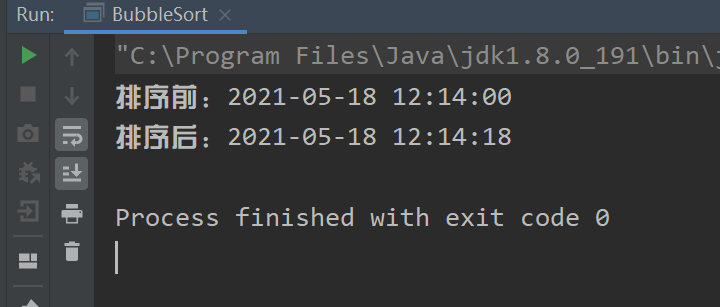
性能测试
这里用8000的数据来测试
package top.lukeewin.demo21;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] a = {2, 5, 1, 8, 6};
//测试一下排序的速度
int[] a = new int[80000];
for (int i = 0; i < 80000; i++) {
a[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 8000000);
}
Date date1 = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String start = simpleDateFormat.format(date1);
System.out.println("排序前:" + start);
//调用排序方法
bubbleSort(a);
Date date2 = new Date();
String end = simpleDateFormat.format(date2);
System.out.println("排序后:" + end);
}
//冒泡排序
public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
int temp = 0;//用于交换
boolean flag = false;//标志位,标志是否是前一个数大于后一个数
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {//趟次
for (int j = 0; j < a.length - i - 1; j++) {//每趟比较的次数
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
flag = true;
//交换
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
if (!flag) {//如果在一趟排序中没有发生交换,那么直接结束最外层循环
break;
} else {
flag = false;
}
}
}
}
视频讲解,我会放到我的B站中,我的B站,大家最好结合着视频学习
Q.E.D.











